CBD (cannabidiol) is a non-psychoactive compound derived from hemp, now found in many wellness products: CBD oils, CBD e-liquids, CBD flowers, herbal teas, gummies, cosmetics, etc. CBD effects and sensations vary widely from one person to another. They depend in particular on the product format, the dosage, the extraction type (full spectrum, broad spectrum, isolate) and individual sensitivity. This article provides a thorough, factual overview, aligned with French regulations, to better understand what you may experience with CBD.
+ Article contents
- How does CBD work in the body?
- The most commonly reported sensations
- Effects depending on the type of CBD
- Effects depending on the form of CBD
- How long before you feel the effects?
- How to tell if CBD is working
- Which product to choose depending on the sensation you’re looking for
- Does CBD get you high?
- Contraindications and precautions
- Our tips for exploring CBD effects
- CBD effects and sensations FAQ
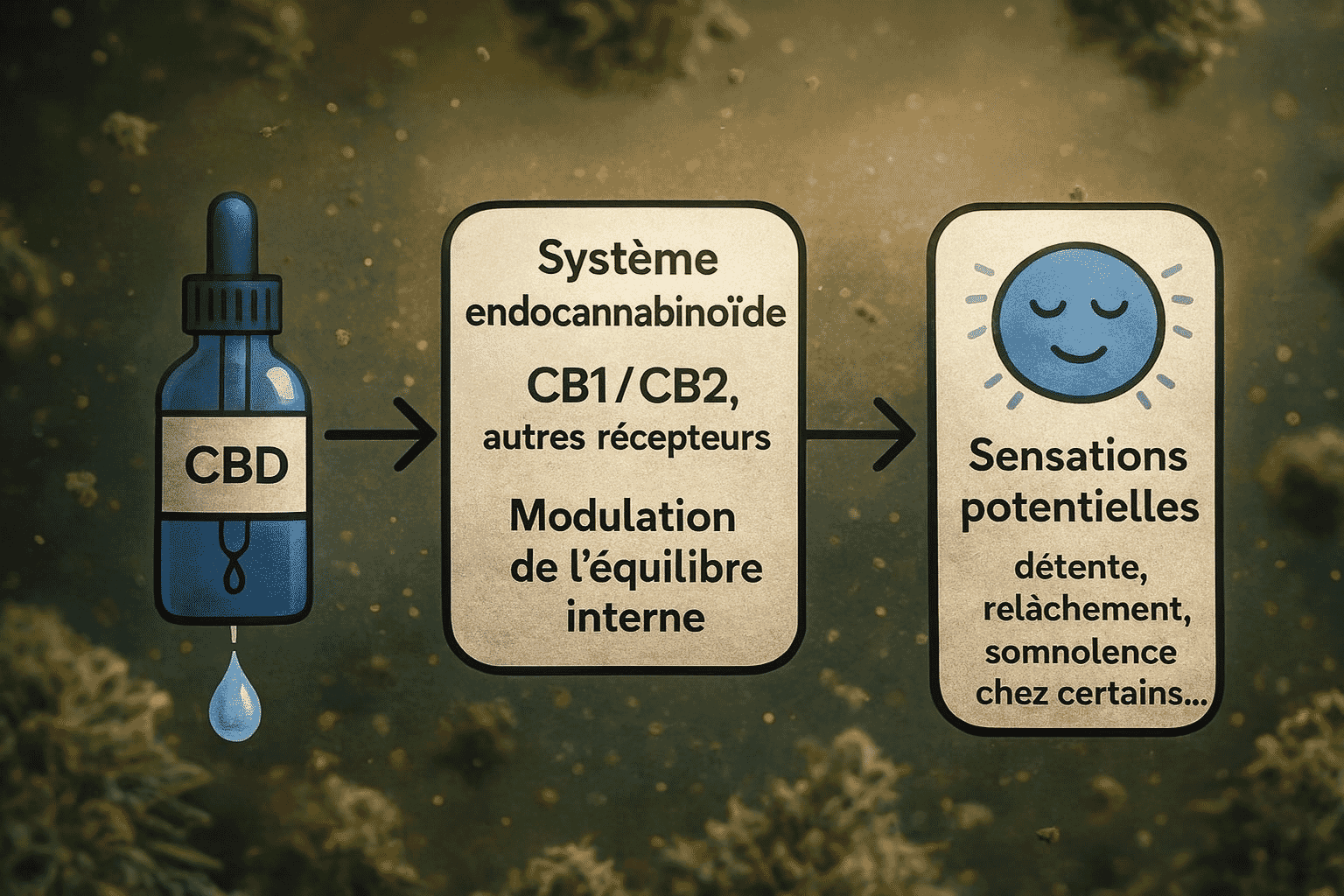
How does CBD work in the body?
CBD interacts with a physiological network called the endocannabinoid system. This system helps maintain homeostasis, meaning the body’s internal balance (mood, sleep, appetite, stress response, physical comfort, etc.).
It mainly relies on two families of receptors:
- CB1, highly present in the central nervous system;
- CB2, more expressed in the immune system and certain peripheral tissues.
Unlike THC, CBD does not directly activate these receptors. Instead, it acts more like a modulator, influencing the activity of the endocannabinoids produced by the body and interacting with other targets (serotonin receptors, GABA, ion channels, etc.).
As a result, the sensations you may feel (relaxation, calmness, possible drowsiness in the evening) can be more or less noticeable depending on the dose, the product, and individual sensitivity.
Start with a small dose of CBD, note how you feel for a few days, then increase gradually until you find your personal threshold—without exceeding the product’s recommendations.
The most commonly reported sensations
Studies and user feedback mostly describe subtle effects. CBD does not usually feel like a “knockout” product, but rather like a gentle adjustment to perception and comfort.
- Mental easing: a feeling of “turning down the volume” of thoughts, without euphoria or major changes in consciousness.
- Muscle relaxation: a sense of a less tense body, lower shoulders, a less clenched jaw.
- A sense of calm: some people feel a bit more distance from everyday stressors.
- Possible drowsiness in the evening: for some, taking CBD later in the day can come with an urge to fall asleep more quickly.
- Soft / “cottony” feeling: described as a gentler ambiance, without a “high.”
Effects depending on the type of CBD (full spectrum, broad spectrum, isolate)
Beyond dosage, the extraction type can also influence sensations. There are three main profiles:
Full-Spectrum CBD
Full spectrum contains CBD, other cannabinoids (CBG, CBC, CBN…), terpenes, and legal trace amounts of THC (within the 0.3% limit for products compliant with French law). It may also include rarer cannabinoids such as cannabicyclol (CBL). Many users describe a more “overall” sensation, sometimes linked to the entourage effect, meaning synergy between hemp compounds.
Broad-Spectrum CBD
Broad spectrum keeps most cannabinoids and terpenes, but is free of detectable THC. It is often chosen by people who want a rich profile while avoiding the presence of THC.
CBD Isolate
Isolate is purified CBD (> 99% CBD). It contains no other cannabinoids or terpenes. The sensation is sometimes described as more “linear”, focusing on cannabidiol alone.
| CBD type | THC present? | Described sensation* | Aromatic richness | Perceived intensity* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full spectrum | Yes, trace amounts (≤ 0.3%) | More “overall,” enveloping effect | High | Moderate to strong depending on dose |
| Broad spectrum | No (0% detectable) | Intermediate, balanced profile | High | Variable |
| Isolate | No | More “pure,” CBD-only sensation | Low | Often more subtle |
*Subjective sensations, varying from one person to another, with no guarantee of effect.
For a more detailed overview, you can read our article on the differences between full-spectrum, broad-spectrum and CBD isolate .
Effects depending on the form of CBD
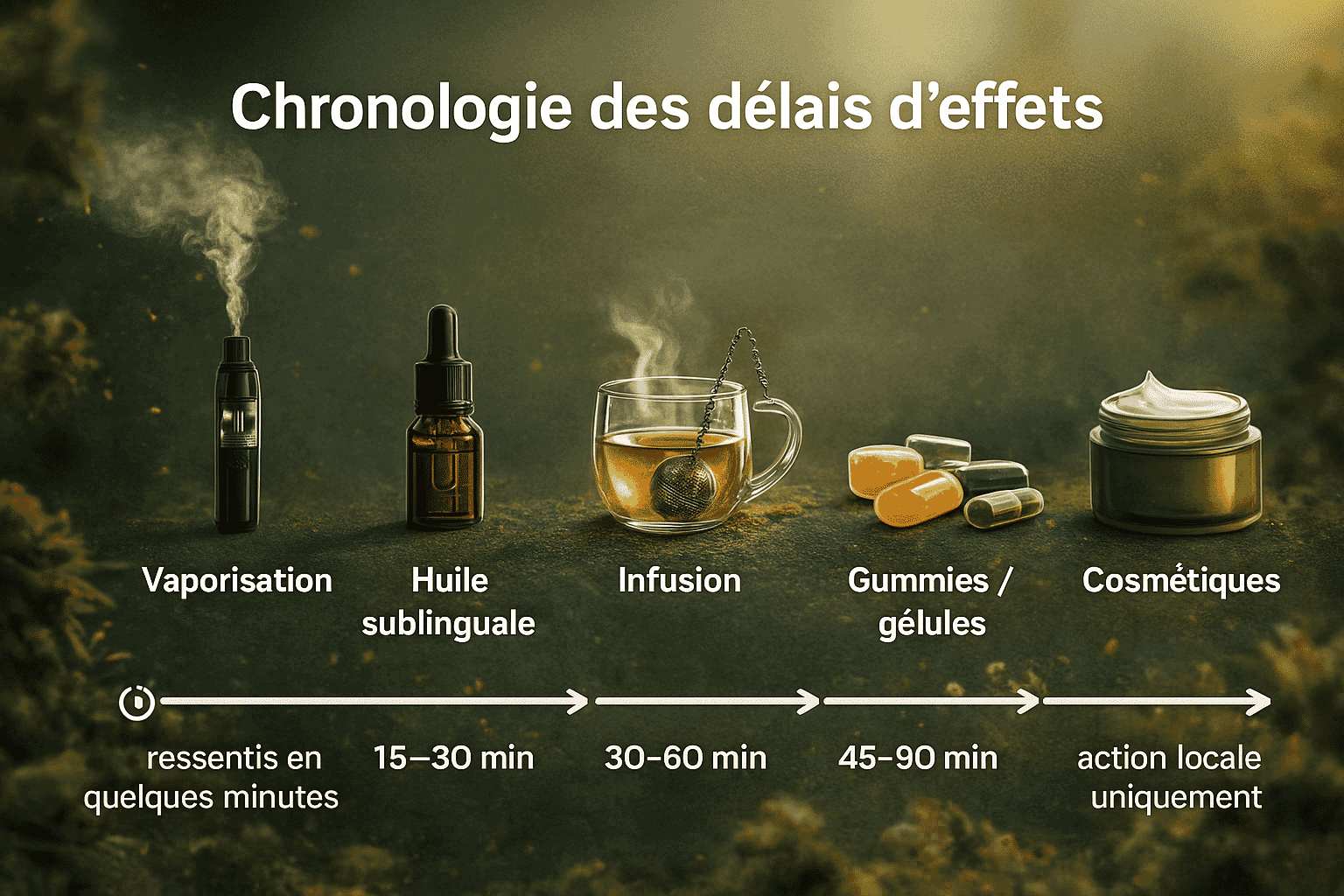
The consumption method affects the speed of onset, perceived intensity, and duration of effects.
Sublingual CBD oils

Oils are generally used under the tongue (sublingual): a few drops held for 60 to 90 seconds before swallowing. Sensations are often reported 15 to 30 minutes after intake. Dosing is relatively precise (number of drops, concentration in mg/ml).
For more practical details, you can read our article on how to use CBD oil .
CBD flowers and resins
.jpg)
CBD flowers or CBD resins can be used by vaporization or incorporated into preparations (infusions, recipes). Vaporization often produces faster and more noticeable effects. It is recommended to avoid combustion, which generates harmful substances (tobacco, smoke).
CBD e-liquids for electronic cigarettes
.jpg)
CBD e-liquids are used with a suitable electronic cigarette. They allow you to inhale CBD as vapor, with sensations generally appearing quickly, similar to vaporizing flowers. Perceived intensity varies depending on concentration in mg/ml, number of puffs, and frequency of use.
CBD infusions

CBD infusions tend to provide a gentle, progressive effect. Sensations generally appear between 30 and 60 minutes, especially if the infusion is consumed with a fatty ingredient (milk, plant-based drink…) which helps dissolve cannabinoids.
Gummies, capsules and other oral forms
.jpg)
Gummies, capsules, or tablets go through digestion. Effects are therefore slower to appear, often between 45 and 90 minutes, but may last for several hours.
CBD cosmetics

CBD creams, balms, and massage oils act locally on the application area. Sensations relate only to skin comfort and the massage feeling, with no psychoactive effect.
For a faster perceived effect, favor the sublingual route (oil under the tongue), vaporizing flowers, or using CBD e-liquids over classic oral forms (gummies, infusions), which act more slowly.
How long before you feel the effects?
The timelines below are approximate ranges. They vary depending on metabolism, food intake, product form, and dose.
| CBD form | Indicative onset time | Perceived duration |
|---|---|---|
| Sublingual oil | 15–30 min | A few hours |
| Vaporization (flowers, CBD e-liquids) | A few minutes to 15 min | About 1 to 3 hours |
| Gummies / capsules | 45–90 min | Up to 6–8 hours depending on dose |
| CBD infusions | 30–60 min | Several hours |
| Cosmetics | Variable (local action) | Limited to the application area |
How to tell if CBD is working
CBD effects are often subtle. Rather than an immediate “before/after,” they may appear as gentle signals within the hour following intake:
- Smoother breathing and a feeling of settling down.
- Physical release, less tense shoulders, a more relaxed jaw.
- Less inner tension, slightly reduced irritability.
- Moderate mental calm, without thoughts disappearing entirely.
For some people, no clear change is felt, even after multiple tries. That doesn’t necessarily mean the product is low quality: CBD does not affect everyone in the same way.
For one week, note each day: CBD form, dose, time taken, context (stress, previous night’s sleep), and how you feel at +30 min, +1 hr, +2 hrs. This helps you see more clearly whether CBD makes a noticeable difference for you—or not.
Which product to choose depending on the sensation you’re looking for
The table below offers a selection guide based on the main sensation you’re seeking. It does not replace medical advice.
| Desired sensation | Commonly chosen forms* | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Relaxation at the end of the day | Sublingual oil, infusion, gummies, CBD e-liquid with light vaping | Take in the evening, moderate dose, calm environment. |
| Calming down after a busy day | Sublingual oil, flower vaporization, CBD e-liquids | Start with a low dose to assess sensitivity. |
| A “cocooning” evening vibe | CBD infusion, gummies, oil + herbal tea | Nice while watching a movie or before bed. |
| Body comfort after sports | CBD cosmetics, massage oil | Local action, massage on worked areas. |
| Occasional relaxation during the day | Low-dose sublingual oil, gummies, CBD e-liquids | Assess the impact on alertness before driving. |
*Usage trends observed among consumers; not a medical recommendation.
To go further, it can be helpful to read an article dedicated to CBD dosage in e-liquids as well as an article about cannabicyclol (CBL), a rare cannabinoid present in some full-spectrum extracts.
You can also explore: our CBD flowers, our CBD resins, our CBD e-liquids and our CBD gummies.
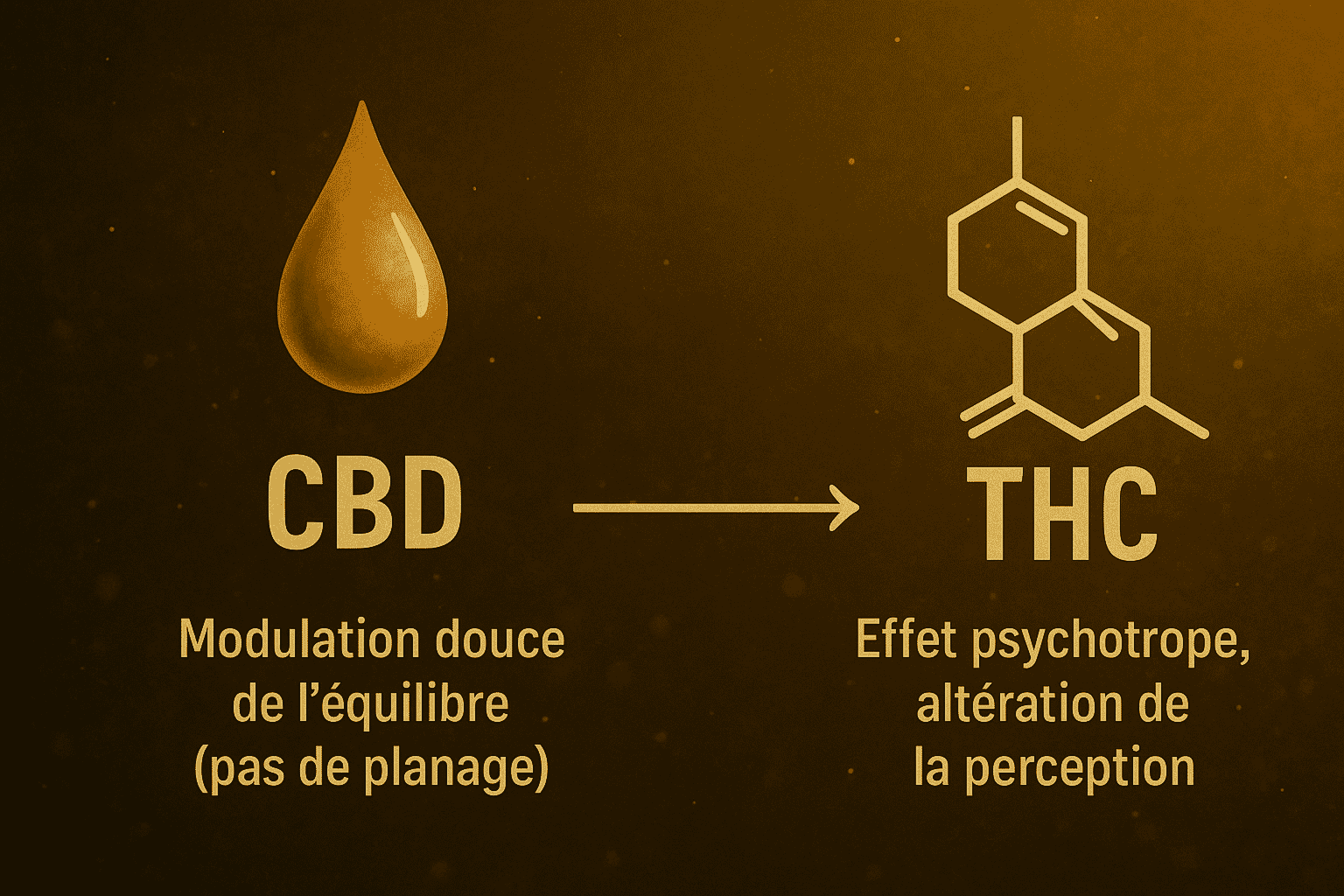
Does CBD get you high?
No. CBD is not psychoactive. At the usual doses found in wellness products compliant with regulations (THC ≤ 0.3%), it does not cause a “high” comparable to THC-rich cannabis.
The main differences with THC can be summarized as follows:
| CBD | THC | |
|---|---|---|
| Psychoactive effect | No (at usual doses) | Yes (high, euphoria, altered perception) |
| Legal status | Allowed under conditions (THC ≤ 0.3%) | Strictly regulated; recreational use prohibited |
| Described sensation | Relaxation, calm, subtle effects | Euphoria, altered state of consciousness |
Contraindications and precautions
CBD has a generally favorable safety profile in available studies, but some situations require extra caution.
- Minors: CBD products are generally not recommended for minors outside a specific medical context.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women: as a precaution, CBD should be avoided during pregnancy and breastfeeding due to insufficient long-term data.
- People on medical treatment: CBD may interact with certain liver enzymes (CYP450) and change how some medicines are metabolized (anticoagulants, antiepileptics, psychotropic drugs, etc.).
- Serious or chronic conditions: medical supervision is essential before introducing CBD.
If you are on medical treatment, have a known health issue, or are unsure, always seek the advice of a healthcare professional before consuming CBD.
Our tips for exploring CBD effects
- Think of CBD as a wellness supplement, not a medicine.
- Choose products with available lab analyses, traceable, and compliant with the legal framework (THC ≤ 0.3%).
- Start with a low dose and increase gradually while monitoring how you feel.
- Give the same routine at least a few days before deciding whether it is useful to you.
- If you experience side effects (marked fatigue, digestive discomfort, etc.), reduce the dose or stop, and seek medical advice.
CBD effects and sensations FAQ
What are the most common effects of CBD?
How long before you feel the effects?
- about 15–30 minutes after taking sublingual oil;
- within a few minutes after vaporizing or taking puffs of CBD e-liquid;
- between 45 and 90 minutes for gummies and capsules;
- between 30 and 60 minutes for infusions.
Why don’t I feel anything with CBD?
- the dose is too low for your weight or tolerance;
- use is too occasional (a single isolated intake);
- the chosen form isn’t the best fit for your goal (oil, e-liquid, infusion, gummies, etc.);
- your body responds weakly to CBD.
Can CBD cause drowsiness?
Does CBD get you high?
Full spectrum, broad spectrum, isolate: what’s the difference in sensations?
- Full spectrum (with legal trace THC) is often associated with a more “overall” sensation.
- Broad spectrum (no detectable THC) offers a rich cannabinoid/terpene profile without THC.
- Isolate focuses only on CBD and is described as more “linear”.
What dosage should I choose?
- start with a low dose (for example a few milligrams per intake);
- keep that dose for a few days while observing how you feel;
- increase gradually as long as tolerance is good.
Is CBD compatible with everyone?
- minors (outside a medical framework);
- pregnant or breastfeeding women;
- people with serious or chronic conditions;
- people on medications potentially affected by interactions.
What are the main scientific sources on CBD?
International sources (journals and reports)
- Lu HC, Mackie K. Review of the Endocannabinoid System. Frontiers in Neuroscience.
- Millar SA et al. A Systematic Review on the Pharmacokinetics of Cannabidiol in Humans. Frontiers in Pharmacology.
- Moltke J, Hindocha C. Reasons for cannabidiol use: a cross-sectional study of CBD users. Journal of Cannabis Research.
- WHO. Cannabidiol (CBD) – Critical Review Report. World Health Organization.
French sources (public institutions)
- Inserm. Overview articles on CBD and the endocannabinoid system (section “Cannabis and health”, Canal Détox).
- ANSM. Press releases and information sheets on cannabidiol and risks of misuse or drug interactions.
- HAS. Opinions and documents relating to cannabidiol-based medicines (e.g., Epidyolex) and medical cannabis.
- French Health Insurance (Ameli). Information sheets on non-medical cannabidiol and precautions for use.
These resources help you dive deeper into how CBD works, its safety profile, and the current state of scientific knowledge. They do not replace a healthcare professional’s advice for an individual situation.
